Uganda’s rapidly growing population presents the country with the challenge of feeding a big population. Yet Uganda’s agriculture is faced with numerous challenges. Below is the guidance in coming up with science-based solutions towards improving food security in Uganda.
(b) The science behind
(i) Food security involves (a) the ability to fill and to re-fill a food reserve (b) the capacity to protect food in the reserve against weather, pests and other bio-destroying agents.
(ii) Drying harvested food off the ground protected food quality, i,e. free of contaminating sand, dirty, etc.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Historical Uganda largely achieved food security. Thus, even in the midst of various challenges facing present Uganda, the country can still achieve food security. Furthermore, Uganda should not entertain excuses for poor quality of food on the market. Either the ways of drying food should be improved or technology should be developed that is able to isolate food from dirty and other contaminants before processing.
(d) What you need to consider
(i) Have you ever heard of hunger in European countries? Yet these countries are faced with winter (very cold season) during which almost no plant is able to grow.
(ii) How about famine in Arab countries? Yet these countries are deserts with limited land to farm.
(iii) Why then should a country like Uganda, with good rains and fertile land, suffer periodic famines?
(iv) What can your generation do to eliminate hunger from Uganda, when it eventually takes charge of the country?
(v) Have you ever taken porridge or eaten a snack and you feel small sand particles crushed between your teeth?
(vi) What is the cause of that problem and how can it be solved?
(b) The science behind
(i) Steaming prevents loss of nutrients in the food.
(ii) Cooking the main food together with accompanying foods meant saving on firewood and thus, conserving the environment that provides cooking energy.
(iii) Eating cooked vegetables minimized risks of infections, given that the hot and wet climate in Uganda may promote germ multiplications on plants.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Uganda’s vegetation is disappearing mainly because of the need for firewood and charcoal. This need calls for efficiency in energy use. The efficiency can be achieved through innovative cooking practices, such as one described above.
(d) What you need to consider
(i) What is the main source of energy for cooking in Uganda?
(ii) Why is the source of energy you mentioned in (i) above widely used in Uganda?
(iii) Does it have any impact on the environment?
(iv) If it has an impact on the environment, what can be done to minimize the impact?
(v) Which sources of energy can be used for cooking while at the same time having less harm on the environment?


(b) The science behind
Changes in pH (acidity/alkalinity) breaks down cow ghee.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Uganda has the challenge of improving on the quality of its local foods, but also improving on their production methods, as countries in Asia have done.
(d) What you need to consider
(i) What does the word pH mean?
(ii) When the pH value is below 7, they say that environment is acidic. What does this mean?
(iii) When it is above 7, they say it is alkaline. Again, what does this mean?
(iv) Why is an alkaline liquid able to break-down cow ghee?
(v) Where else do we find alkaline or acidic liquids used in breaking down things?
(vi) How are acidic or alkaline liquids produced?
(vii) What are other purposes for acidic or alkaline liquids?
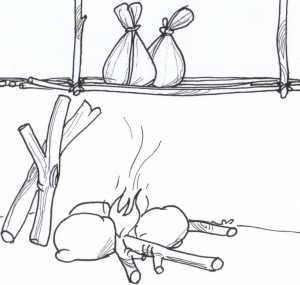
(b) The science behind
(i) Vegetables are an important source of food nutrients such as iron. These nutrients are needed in smaller amounts (micronutrients) by our bodies to enable us live a healthy life.
(ii) Storage above the fireplace protected the vegetables against insect pests and other bio-destroying agents.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Many pregnant women and children under 5 years of age in Uganda lack micronutrients such as iron, rendering their bodies weak and vulnerable to diseases. Yet, Uganda is blessed with abundant vegetables and fruits that are natural sources of micronutrients. Addressing this challenge requires health education, but also innovative ways of preserving and storing fruits and vegetables for consumption during off seasons.
(d) What you need to think about
(i) Did you know that fruits and green vegetables are an important source of natural medicines (micronutrients) for our bodies?
(ii) How often do you eat them? The more often you eat them, the better.
(iii) Have you ever thought of planting a tree, especially a fruit tree?
(iv) If yes, do not stop at thinking; do it, i.e. plant it every time you celebrate your birthday.
You can promote food security in Uganda by interesting students in your school into demonstrating and explaining remarkable food practices, such as the ones described above. This is possible, especially if you a member to any of the following school clubs:
- Patriotism Club
- Science Club
- Writers’ Club
Becoming wealthy or an influential Person
Behind food challenges facing Uganda are opportunities for creating jobs or starting a business. Look around carefully for any of these opportunities. The subsections “What you need to consider”, previous page, may provide you with a starting point in identifying these opportunities. If you detect an opportunity, and it sounds interesting to you, take it up as follows:
i. Write it down on paper.
ii. Revisit it after a week and see if it still makes sense.
iii. If the idea still makes sense, get more information about it, especially through reading.
iv. Use the new information to refine your idea (make it clearer).
v. Keep it for an appropriate time.
In short, you can seize that opportunity while you are still at school, then turn it into a business or job after you have completed school or during your long school holidays. This is one of the surest paths before you towards becoming a wealthy or an influential person in Uganda and beyond.
By reading this interesting story and changing accordingly, you will become valuable to efforts of achieving food security in Uganda.
Careers relevant to Food security in Uganda
If you want to establish whether or not nutrition, food production and food preservation are areas you can work in after school, read this interesting story. Some of the careers relevant to food security in Uganda include:
| Career | Description |
| Agricultural technician | -Assists agriculturists in their work and helps with the collection of information. |
| Agricultural engineer | -Applies engineering principles of science and technology, as well as their knowledge of agricultural practice, to agricultural problems. |
| Agricultural extension officer | -A person between research and farmers. He informs agricultural researchers the problems farmers face. He guides farmers into using solutions or new technologies that agricultural research has produced. |
| Agricultural-economist | -Concerned with all economical activities that influence agriculture, and aims at making it more viable/profitable. |
| Animal scientist | -Works to develop better ways of making meat, poultry, eggs and milk. They also inspect and grade food products. |
| Crop scientist/Agronomist | -Helps farmers grow more and better food, but while preserving our natural resources. |
| Farmer | -Grows crops and raises animals for food production. |
| Food scientist/technologist | -Tries to create food products that are healthier, safe, tastier, and easy to use. |
| Forester | -Manages forested lands for economic, recreational, and conservation purposes. |
| Grain grader | -Responsible for the grading, storage and distribution of food grain. |
| Soil scientist | -Studies what is in soils, and how soils help plants grow. They see how things like fertilizer can improve soils. |
| Veterinarian | -Takes care of sick and injured animals. |