Environment means the living and non-living things that surround us. If this environment is not protected, your life too will be at a risk of coming to an end. Environmental protection is therefore something that the world takes seriously. In other words, it has many opportunities for earning income. Below is the guidance in coming up with science-based solutions towards protecting the environment.
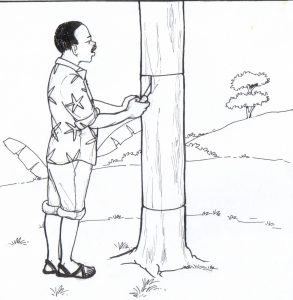
-The exposed tree-trunk was wrapped with fresh banana leaves and left for 3 – 4 days to dry.

(b) The science behind
We should use biological resources in such away that tomorrow’s generation will find them and use them too. This is what they call using biological resources in a sustainable way.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Uganda is facing increasing demand for firewood, timber, cultivation land, grazing land, etc. Most of these demands will be addressed through sustainable use of biological resources.
(d) What you need to consider
i. Have you ever used any biological resource(s)?
ii. If yes, what should be done to ensure that your children too can find and use that biological resource?
iii. Can you, as you grow up, become an advocate for your answer to question (ii) above?
(b) The science behind
Top soil is rich in humus and other soil nutrients. Unfortunately, it is lost easily through soil erosion. Good farming practices in traditional Uganda, such as the ones described above, prevented or minimized soil erosion.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Soil erosion is a big problem in Uganda, as evidenced in the muddy water flowing in many of our rivers. Promoting good farming methods, like was the case in traditional Uganda, will go a long way in reducing soil erosion.
(d) What you need to consider
(i) Is there anything you can do to prevent soil erosion at your home or school?
(ii) If you come up with an idea that can prevent soil erosion, ask your teacher or parent for permission to implement it – and then see if it works.
(iii) If it works, write it down and keep it. You may make money out of it, after finishing school.

(b) The science behind
An innovative approach to conserve water sources among local communities. Discouraging the fetching of water in a hot day sun-shine was away of minimizing chances to get bitten by snakes and other poisonous reptiles, living in the conserved habitat. Repeated bites from poisonous reptiles would have forced the community to clear the conserved vegetation.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
-Many of Uganda’s springs, streams and rivers are around because their water sources or their catchments areas were conserved by our fore fathers. Unless present Uganda does the same, upcoming generations may face a big problem of water scarcity.
-Local communities should be allowed to use resources in national parks and other conserved areas. What needs to be regulated is the use of conserved resources by these communities. If allowed access to conserved resources, local communities will become better partners in conservation campaigns.
(d) What you need to think about
i. Do you bathe or wash your body every day?
ii. Did you know that bathing every day may not be possible in the future? In other words, that the increasing water scarcity may force people, including you, to bathe once or twice a week?
iii. You can help prevent that situation by using water sparingly, by promoting the harvest of rain water for use, by educating communities to preserve vegetation around water sources and most importantly, by planting a tree every time you celebrate your birth day.
(b) The Science Behind
A novel practice to conserve local biodiversity (animals and plants) for present and future generations.
(c) Challenge for present Uganda
Local communities, if well mobilized, can play an important role in the restoration and conservation of biodiversity in Uganda.
(d) What you need to think about
i. Does your mother’s or father’s ethnic group have any practice(s) that conserve nature?
ii. If yes, which ones?
iii. Which of those practices could be promoted in present times?
iv. Do you know that you can make a living, after finishing school, by promoting conservation practice(s) you identified in (iii) above?
You can stimulate the search for new and better ways of conserving the environment in Uganda by interesting students in your school into demonstrating and explaining community practices that conserved nature, such as the ones described above. This is possible, especially if you a member to any of the following school clubs:
- Science Club
- Environment Club
- Patriotism Club
- Wildlife Club
- Writers’ Club
- Computer Club
- Debating Club
Becoming an influential person
Most environmental challenges facing Uganda show work in waiting for young people like you. Behind some of these challenges are opportunities to create jobs for yourselves. Look around carefully for any of these opportunities. The subsections “What you need to consider”, previous page, may provide you with a starting point in identifying these opportunities. If you notice an opportunity, and it sounds interesting to you, take it up as follows:
i. Write it down on paper.
ii. Revisit it after some time and see if it still makes sense.
iii. If the idea still makes sense, get more information about it through reading or asking others.
iv. Use that information to refine your idea (make it clearer for yourself).
v. Keep it for an appropriate time.
In brief, you can seize that opportunity while you are still at school, then turn it into jobs after completing school. This is one of the shortest paths before you towards becoming an influential person in Uganda.
By reading this interesting story and changing accordingly, you will become valuable to efforts of conserving the environment in your country.
Careers relevant to environmental conservation
If you want to establish whether or not environment conservation is an area you could work in after finishing school, read this interesting story. Some of the careers through which you can participate in conservation of the environment include:
| Career |
Description |
| Aquatic scientist | -Studies the physical, chemical, biological and ecological aspects of inland and marine water environments. |
| Biologist | -Studies the origin, relationships, development, anatomy, functions, heredity and other basic characteristics of plant, animal and microbial life. |
| Botanist | -Studies a whole range of plant organisms; algae, fungi, mosses, ferns, gymnosperms and flowering plants. |
| Chemical engineer | -Designs and operates processes for large scale production of chemicals, plastics, minerals and other useful commodities. |
| Ecologist | -Studies the interactions between living organisms and their environment, and between the organisms themselves. |
| Entomologist | -Studies insects, especially those of vital importance to man, such as vectors and pests. |
| Environmental health officer | -Responsible for the management of environmental affairs that have an influence on the human well-being. |
| Environmental scientist | -Finds and fixes pollution and other environmental problems. |
| Farmer | -Grows crops and raises animals for food production. |
| Forester | -Manages forested lands for economic, recreational, and conservation purposes. |
| Geneticist | -Studies the way hereditary qualities are transmitted in living organisms. |
| Geographer | -Studies the total relationship between people and their environment. |
| Herpetologist | -Studies reptiles and amphibians, for example lizards, tortoises, snakes, crocodiles, frogs, toads and salamanders. |
| Ichthyologist | -Studies the fundamental aspects of fish biology. |
| Land surveyor | -Measures and draws what the earth’s surface looks like; may put the outcomes in deeds, leases, and other legal documents. |
| Landscape architect | -Makes outdoor places such as parks, playgrounds, schools, shopping centers, backyards, more beautiful and useful. |
| Mathematician | -Creates, investigates and analyzes mathematical structures in order to solve and understand mathematical problems. |
| Meteorologist | -Studies the earth’s atmosphere and its changes. |
| Molecular biologist/biotechnologist | -Develops methods to control biological processes for use in industry, agriculture, forestry, horticulture and breeding. |
| Nature conservation officer | -Seeks to conserve natural resources through sustainable use. |
| Oceanographer | -Studies the sea and all its different facets such as the sea floor, marine life, ocean currents, the physical and chemical composition of the water and also the air above the ocean. |
| Ornithologist | -Studies the behavior, ecology, physiology, classification and conservation of birds. |
| Soil scientist | -Studies what is in soils, and how soils help plants grow. They see how things like fertilizer can improve soils. |
| Urban planner | -Figures out the best way to use the land in cities and neighborhoods. |
| Veterinarian | -Takes care of sick and injured animals. |
| Zoologist | -Involved in the study of animals. |